MongoDB Overview
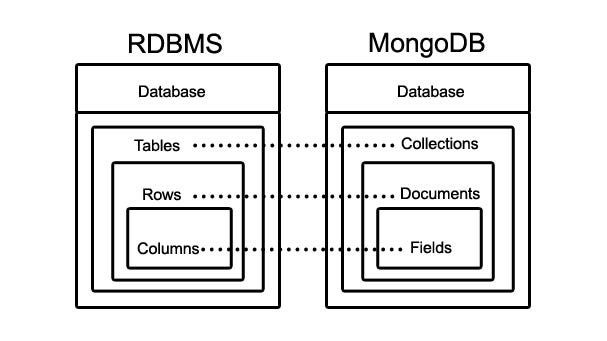
MongoDB is an open source, cross platform, document oriented NoSQL database that stores data in the form of documents and collections. A document is nothing but a record, that contains all information about itself. A group of documents, is called a collection.
A document can contain a number of fields (value), regarding the details of the record. One document size can be different from the other as two different documents can store varied number of fields. Every field (value) has an associated key mapped to it. The field can be of any data type like the general text, number, etc. A field can also be a link to another document or arrays. MongoDB uses BSON (binary encoding form of JSON), to include additional data types like date, that is not compatible with JSON.
Features
- Scalability:- MongoDB is a specialized database for BigData processing. It can contain large volumes of data, therefore making it highly scalable.
- Flexibility:- MongodB is schema-less which means it doesn’t enforce relations between fields, rather allows the storage of values of any data type, in a stream.
- Sharding:- Sharding is an interesting and a very powerful methodology in MongoDB. MongoDB allows distribution of data onto several servers, as opposed to a single server.
- Data replication and recovery:- MongoDB provides specialized tools for data replication, as a backup, in times of any system failure.
- High Performance and Speed:- MongoDB supports different features like dynamic ad-hoc querying, indexing for faster search functionality, tools like Aggregation pipeline for aggregation queries etc.
MongoDB Database
